6.2: Communications Process
- Page ID
- 94904
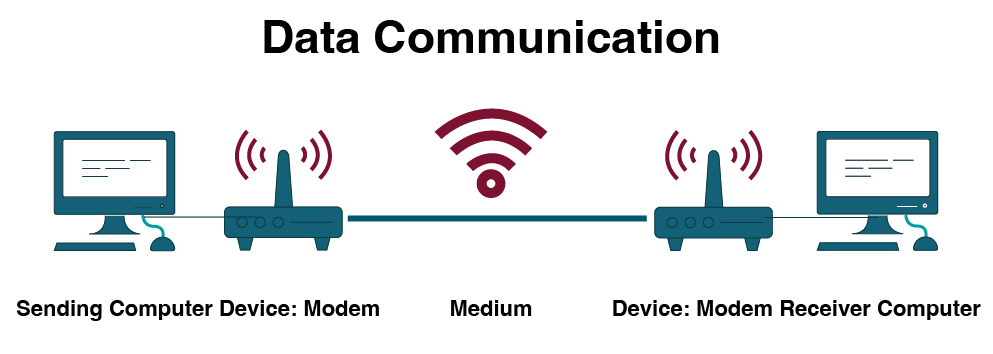
Before delving into the details of networking, it is important to understand how data is communicated between computers. Data communication is the electronic transmission of encoded information to, from and between computers. Data communication requires a number of devices in order for information to be transferred. The process begins when a computer sends an instruction to transmit information.
- A modem converts the format of the data so it may be transmitted between computers.
- A medium provides a path for signals to be transmitted. This can be in a physical format like copper cable, coaxial cable or fibre optics. It can also be radiated or wireless.
- The receiving computer accepts the transmission.
In communicating data, speed is important. The amount of data that can be transferred from one point to another in a certain period of time is referred to as bandwidth. Bandwidth can be narrow or broad, and it depends on the access technology. Broadband is when a high amount of data is transmitted simultaneously by digital subscriber line, cable and fibre optic technologies. Narrowband is when a limited amount of data is transferred over a specified time period.
Communication Through the Ages
Communication modes and technologies have changed dramatically over time from cave paintings to social media platforms. To check out the history of communication review this communication timeline from BizTech Magazine.


