11.3: Units
- Page ID
- 14980
A very powerful part of Mathcad comes from its ability to handle units and unit conversions. When entering an equation, you can access the complete set of units under the menu at Insert > Units
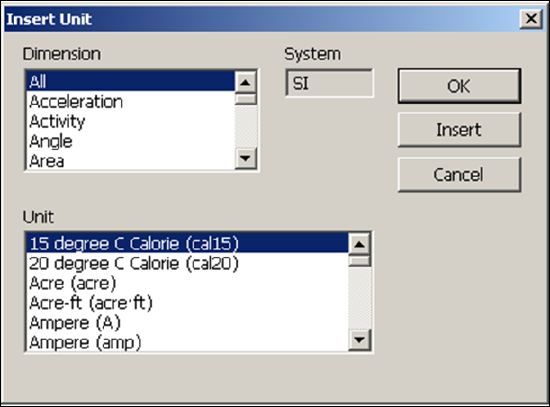
or if you know the name of the unit, you can just type it in:
\[Volume:=34gal\nonumber\]
\[Volume=128.704L\nonumber\]
\[Distance:=10ft\nonumber\]
\[Distance=3.048m\nonumber\]
In this example, we entered the first and third lines exactly as they look, using the colon to make the assignment equals sign := and typing the letters “gal” and “ft”. In the second and fourth equations, we used the evaluation equals sign = to calculate. Note that Mathcad automatically calculates using metric units as a default. To keep an expression with a specific unit, consider the following example where we want the final answer in feet. We want to calculate the distance travelled by an object moving at 10 feet per second for 15 minutes.
We enter the corresponding variables using the assignment equals in defining Velocity, Time and Distance. But, in the fourth line, when we use the evaluation equals, Mathcad automatically converts Distance to meters. To adjust this, first, click at the end of the line where Distance is computed. A small black box appears that we select...

... type ft in the box:
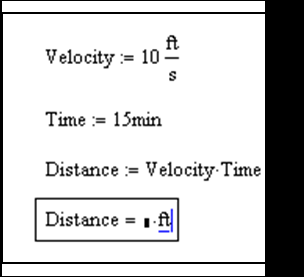
... and hit return:



