1.4: Sources of Energy
- Page ID
- 47153
Energy is stored and available in different forms and sources. These sources are divided into two main groups: renewable and nonrenewable.
1. Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy sources can be replenished repeatedly. Examples include hydropower, solar, and wind energy from the Earth, biomass from plants, and nuclear fusion. These sources are commonly converted into electricity or thermal energy.
2. Nonrenewable Energy Sources
Nonrenewable energy sources cannot be replenished repeatedly. Examples include fossil fuels (natural gas, petroleum oil, coal), tar sands, and uranium (which is used for nuclear fission). These sources are commonly converted into electricity and mechanical (kinetic and potential) energy.
Our world mostly relies on nonrenewable energy sources.
Fossil Fuel Distribution
Fossil fuels are formed over millions of years by the combination of thermal energy from the Earth's core and pressure from rock and soil on the remains (fossils) of dead plants and animals. Fossil fuels are not distributed uniformly over the Earth's surface, as certain parts of the land millions of years ago had more favorable conditions for organisms to grow. Thus, certain parts of the world are richer in fossil fuels than others. Figure 1.4.1 shows a rough distribution of fossil fuels on Earth.
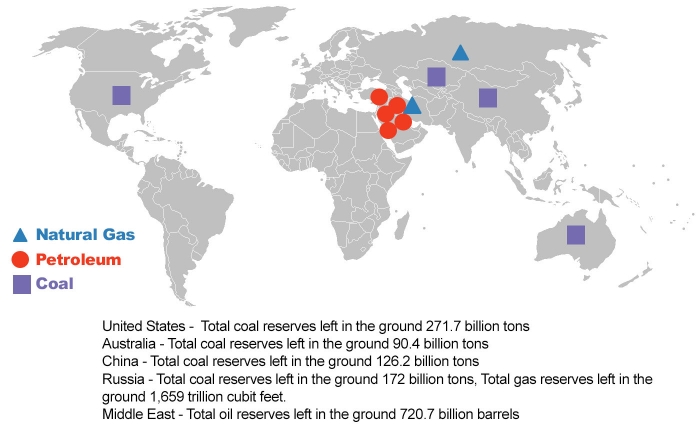
Figure 1.4.1. Fossil fuel distribution across different parts of the world, and quantities of fossil fuels remaining.
Credit: Roke [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons


