10.6: Resolution and Imaging
- Page ID
- 8232
The limit of resolution (or resolving power) is a measure of the ability of the objective lens to separate in the image adjacent details that are present in the object. It is the distance between two points in the object that are just resolved in the image. The resolving power of an optical system is ultimately limited by diffraction by the aperture. Thus an optical system cannot form a perfect image of a point.
For resolution to occur, at least the direct beam and the first-order diffracted beam must be collected by the objective. If the lens aperture is too small, only the direct beam is collected and the resolution is lost.
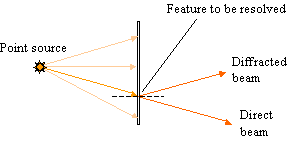
Consider a grating of spacing d illuminated by light of wavelength λ, at an angle of incidence i.
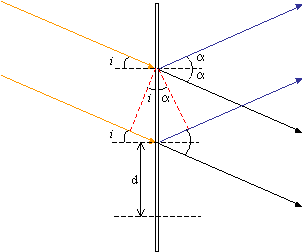
The path difference between the direct beam and the first-order diffracted beam is exactly one wavelength, λ. So,
d sin i + d sin α = λ
where 2α is the angle through which the first-order beam is diffracted. Since the two beams are just collected by the objective, i = α, thus the limit of resolution is,
\[d_{min} = \frac{\lambda}{2 \sin \alpha} \]
The wavelength of light is an important factor in the resolution of a microscope. Shorter wavelengths yield higher resolution. The greatest resolving power in optical microscopy requires near-ultraviolet light, the shortest effective visible imaging wavelength.
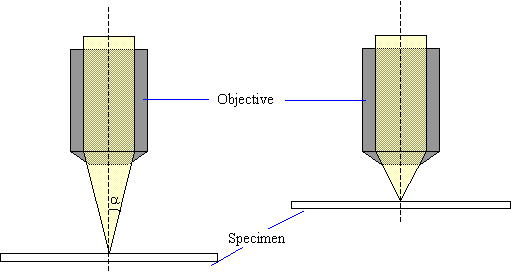
Numerical Aperture
The numerical aperture of a microscope objective is a measure of its ability to resolve fine specimen detail. The value for the numerical aperture is given by,
Numerical Aperture (NA) = n sin α
where n is the refractive index and equal to 1 for air and α is the half angle subtended by rays entering the objective lens.
Numerical aperture determines the resolving power of an objective, the higher the numerical aperture of the system, the better the resolution.
|
Low numerical aperture |
High numerical aperture |
Airy Discs
When light from the various points of a specimen passes through the objective and an image is created, the various points in the specimen appear as small patterns in the image. These are known as Airy discs. The phenomenon is caused by diffraction of light as it passes through the circular aperture of the objective.
Airy discs consist of small, concentric light and dark circles. The smaller the Airy discs projected by an objective in forming the image, the more detail of the specimen is discernible. Objective lenses of higher numerical aperture are capable of producing smaller Airy discs, and therefore can distinguish finer detail in the specimen.
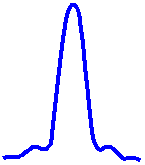
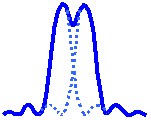
The limit at which two Airy discs can be resolved into separate entities is often called the Rayleigh criterion. This is when the first diffraction minimum of the image of one source point coincides with the maximum of another.
 |
 |
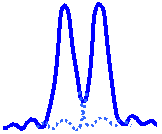 |
| Unresolvable | Rayleigh Criterion | Resolvable |
Circular apertures produce diffraction patterns with circular symmetry. Mathematical analysis gives the equation,
\[d_{min} = \frac{\lambda}{2 \sin \alpha} \]
\[\sin{\theta_R} = 1.22 \frac{\lambda}{d} \]
θR is the angular position of the first order diffraction minimum (the first dark ring)
λ is the wavelength of the incident light
d is the diameter of the aperture
From the equation it can be seen that the radius of the central maximum is directly proportional to λ/d. So, the maximum is more spread out for longer wavelengths and/or smaller apertures.
The primary minimum sets a limit to the useful magnification of the objective lens. A point source of light produced by the lens is always seen as a central spot, and second and higher order maxima, which is only avoided if the lens is of infinite diameter. Two objects separated by a distance less than θR cannot be resolved.


