5.6: Key equations
- Page ID
- 88850
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \) \( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)\(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)\(\newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
Constant-pressure and constant-volume specific heats
| Constant-pressure specific heat | 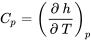 |
|---|---|
| Constant-volume specific heat | 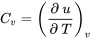 |
Relations between 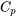 and and 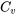 for ideal gases for ideal gases |
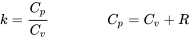
\[C_v=\displaystyle\frac{R}{k-1} \qquad C_p=\displaystyle\frac{kR}{k-1}\] |
Specific enthalpy
| Change in specific enthalpy | 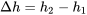 |
|---|---|
| Change in specific enthalpy for ideal gases | 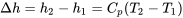 (assuming constant 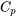 in the temperature range) in the temperature range) |
Relation between 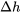 and and 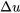 for solids and liquids for solids and liquids |
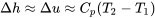 |
Mass conservation equations in a control volume
| Volume flow rate | 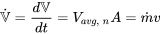 |
|---|---|
| Mass flow rate | 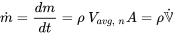 |
| Transient flow | 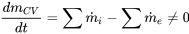 |
| Steady flow | 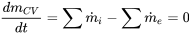 |
Energy conservation equations in a control volume
| Transient flow | 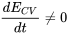
\[\begin{align*} \displaystyle\frac{dE_{CV}}{dt}={\dot{Q}}_{cv}-{\dot{W}}_{cv} &+\sum{{\dot{m}}_i(h_i+\frac{1}{2}V_i^2+gz_i)} \\&-\sum{{\dot{m}}_e(h_e+\frac{1}{2}V_e^2+gz_e)} \end{align*}\] |
|---|---|
| Steady flow | 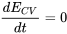
\[{\dot{Q}}_{cv} +\sum (click for details) \]
Callstack:
at (Bookshelves/Mechanical_Engineering/Introduction_to_Engineering_Thermodynamics_(Yan)/05:_The_First_Law_of_Thermodynamics_for_a_Control_Volume/5.06:_Key_equations), /content/body/div[4]/table/tbody/tr[2]/td/p/span, line 1, column 1
|
Mass and energy conservation equations for steady-state, steady-flow (SSSF) devices
| SSSF device | Assumptions | Mass conservation | Energy conservation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Expansion device | Adiabatic flow; Negligible work transfer with the surroundings; Negligible changes in kinetic and potential energies | 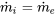 |
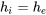 |
| Nozzle and diffuser | Adiabatic flow; Negligible work transfer with the surroundings; Negligible change in potential energy | 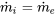 |
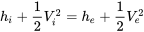 |
| Mixing chamber | Negligible work transfer with the surroundings; Negligible changes in kinetic and potential energies | 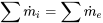 |
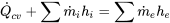 |
| Heat exchanger | Negligible work transfer with the surroundings; Negligible changes in kinetic and potential energies | 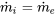 (for each of the hot and cold streams, separately) |
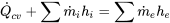 |
| Turbine | Adiabatic flow; Negligible changes in kinetic and potential energies | 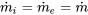 |
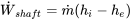 |
| Compressor | Adiabatic flow; Negligible changes in kinetic and potential energies | 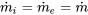 |
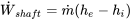 |


